In today’s fast-paced agribusiness landscape, the significance of efficient and sustainable agricultural procurement cannot be overstated. It is a critical link that connects producers and buyers, ensuring the seamless flow of commodities from farm to market. However, traditional procurement practices often grapple with a multitude of challenges, hindering efficiency, cost reduction, and revenue generation for all parties involved.
Producers and buyers face an array of challenges when it comes to agricultural procurement. Inefficient supply chain processes, fragmented communication, and outdated record-keeping systems result in delays, errors, and increased costs. These bottlenecks not only impede operational effectiveness but also hinder efforts to achieve cost reductions and maximize revenue. Moreover, the lack of transparency and traceability in procurement practices raises sustainability and ethical concerns, thereby impacting the reputation and market position of agricultural stakeholders.
Digital technologies have emerged as a game-changer, offering innovative solutions to address the challenges faced by the agricultural industry. Leveraging cutting-edge tools like artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and blockchain, stakeholders can reshape the landscape of agricultural procurement. Real-time data collection, analysis, and sharing empower decision-makers with actionable insights, leading to informed choices. Improved transparency and traceability foster trust and accountability throughout the supply chain, addressing sustainability concerns and bolstering the industry’s reputation.
In the realm of digital solutions for agricultural procurement, AGnimble takes center stage as a pioneering platform. Developed by industry experts, AGnimble is using technologies to streamline procurement processes and optimize outcomes. Its user-friendly interface facilitates seamless communication and collaboration between producers and buyers, eliminating information gaps and minimizing transaction costs. AGnimble empowers stakeholders to access real-time market data, negotiate fair prices, track product quality, and ensure compliance with sustainability standards.
Sustainable Agricultural procurement
Within the domain of agricultural commodity procurement, a multitude of persistent challenges hinder the industry’s progress towards sustainability and reaching its maximum potential. These hurdles necessitate inventive solutions to revolutionize the current landscape, cultivating an environment that excels in efficiency, transparency, and environmental stewardship.
According to a report by the Food & Agriculture Organization (FAO), inefficient agricultural supply chains lead to losses of up to 40% of food produced globally, exacerbating food security concerns. These inefficiencies also hinder the ability to respond effectively to market demands and maintain competitive advantage. Unsustainable procurement practices also have far-reaching environmental and social implications. Consistent procurement/demand of products with low traceability indirectly encourages the excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides in conventional farming methods contributing to soil degradation and water pollution, ultimately compromising the long-term viability of agricultural production. Moreover, unsustainable procurement practices often result in inequitable distribution of resources and exacerbate socioeconomic disparities within rural communities.
The International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) estimates that around 80% of the food in sub-Saharan Africa and parts of Asia is produced by smallholder farmers, who often face challenges accessing markets and obtaining fair prices for their produce.
Another study conducted by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), validated the potential of digital technologies to revolutionize the agri-food sector, enhancing productivity, efficiency, and sustainability. By adopting these technologies, stakeholders can overcome traditional barriers, along with the environmental and social implications of unsustainable procurement, strengthen linkages between producers and processors/the end market and unlock new opportunities for growth and development.
Harnessing the Power of Digital Technologies
Digital transformation is reshaping the agricultural industry, with key trends and drivers propelling its adoption in procurement practices. Factors such as the increasing availability of affordable mobile devices, the growth of internet connectivity in rural areas, and the rise of data analytics capabilities are driving the digital revolution in agriculture. These trends enable stakeholders to collect, analyze, and leverage data to make informed decisions and optimize procurement processes.
Digital technologies offer a multitude of benefits that contribute to sustainable agricultural procurement practices.
- Transparency and traceability in the supply chain: Digital platforms provide transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain, ensuring accountability and ethical sourcing. Blockchain technology, for instance, enables the recording of every transaction, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of information. This transparency helps build trust among stakeholders and provides consumers with the assurance of sustainable and responsibly sourced products (FoodLogiQ).
- Real-time data analytics for informed decision-making: The availability of real-time data analytics empowers stakeholders to make data-driven decisions. Advanced analytics tools can process vast amounts of data, providing valuable insights into market trends, demand patterns, and production efficiencies. This enables proactive decision-making, optimizing procurement strategies, and minimizing waste (Accenture).
- Streamlined processes and increased operational efficiency: Digital technologies streamline procurement processes, eliminating inefficiencies and reducing costs. For instance, cloud-based platforms enable seamless collaboration and communication among stakeholders, reducing paperwork and manual errors. Automation of routine tasks improves operational efficiency, allowing stakeholders to focus on strategic activities (McKinsey & Company).
Overcoming Challenges in Adopting Digital Technologies
Data privacy and security concerns in agricultural procurement: As digital technologies become increasingly integrated into agricultural procurement, data privacy and security concerns must be addressed. The collection and storage of sensitive data, such as farmer/seller/buyer information, production records, and financial transactions, pose potential risks if not adequately protected. The agricultural sector faces cyber threats due to its interconnectedness and valuable data. Robust data privacy measures, encryption, secure storage, and compliance with regulations are crucial. Compliance with data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), is also crucial to safeguarding personal information and maintaining stakeholder trust. Partnerships with technology providers and with a reliable cybersecurity infrastructure are essential steps in mitigating data privacy and security risks.
Addressing infrastructure limitations in rural areas: One of the challenges in adopting digital technologies for agricultural procurement is the limited infrastructure in rural areas. Access to reliable internet connectivity and electricity can be a significant barrier, hindering the widespread adoption of digital solutions. However, efforts are being made to bridge this gap. For instance, initiatives like the World Bank’s Rural e-Commerce Project are investing in improving rural connectivity and building digital infrastructure to enable digital access for farmers and stakeholders in remote areas.
Ensuring inclusivity and accessibility for all stakeholders: In the pursuit of digital transformation, it is crucial to ensure inclusivity and accessibility for all stakeholders. This includes smallholder farmers, who often lack access to technology and face barriers in adopting digital solutions. Efforts must be made to provide training and support to empower these farmers and other stakeholders to embrace digital technologies. Collaborative partnerships between governments, private sector entities, and non-governmental organizations are essential in driving inclusive digital transformation and bridging the digital divide(International Finance Corporation, 2021).
Enhancing Efficiency through AGnimble
AGnimble’s platform offers a comprehensive solution that improves the procurement process for food and agricultural commodities. By utilizing AGnimble’s modern business tools, businesses can source, procure, manage producers, pay, manage inventory and collaborate all in one seamless platform. Our platform is positioned to enhance the global food and agricultural commodity supply chain by connecting the key players to transact in a transparent and sustainable way.
With AGnimble, manual compliance processes are automated reducing the risk of errors and delays. For instance, the producers and buyers can manage documentation required for regulatory compliance, such as import permits, Bill of Lading, certificates of analysis etc. This automation minimizes the time and effort spent on paperwork, allowing importers and exporters to focus on core business activities. Real-time data insights provided by the platform enable importers to make data-driven decisions, optimizing their procurement strategies and identifying opportunities for improvement.
Cost Reduction and revenue maximization with AGnimble
AGnimble’s platform cuts procurement costs through reduced manual work, errors, delays, transactional expenses, overstocking, and helps secure competitive pricing for efficient procurement budgets.
The optimization of supply chain processes not only reduces costs but also enables revenue growth for both producers, exporters and Importers.
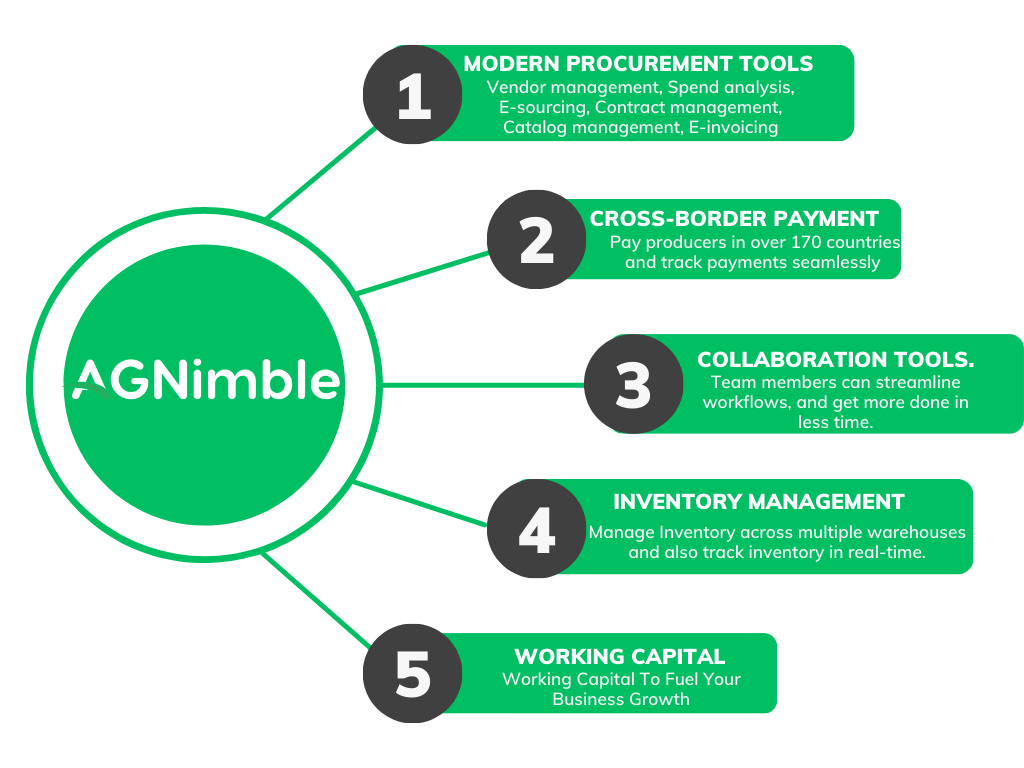
AGnimble’s sustainable procurement digital solutions.
How AGnimble Streamline Coffee Supply Chain
AGnimble streamlines the coffee supply chain by facilitating seamless collaboration and business transactions among the key participants in the value chain, including farmers, exporters, importers, and roasters. This streamlined communication processes reduce the need for lengthy email chains and phone calls, saving time and reducing the chances of miscommunication. With AGnimble, a Green Coffee exporter can effortlessly add all their farmers, along with relevant information such as crop details, farm names, harvest dates, and the anticipated size of the next harvest and conveniently make payments to farmers once the crops are harvested.
In addition, AGnimble serves as a marketplace, enabling exporters listing purchased green coffee from farmers on its platform. Each listing includes a unique Trace ID associated with the specific crop, ensuring buyers have access to comprehensive traceability information for review before making a purchase. The platform also offers a dedicated dashboard for farmers, where they can easily collaborate with buyers and track revenue, in a user-friendly interface.
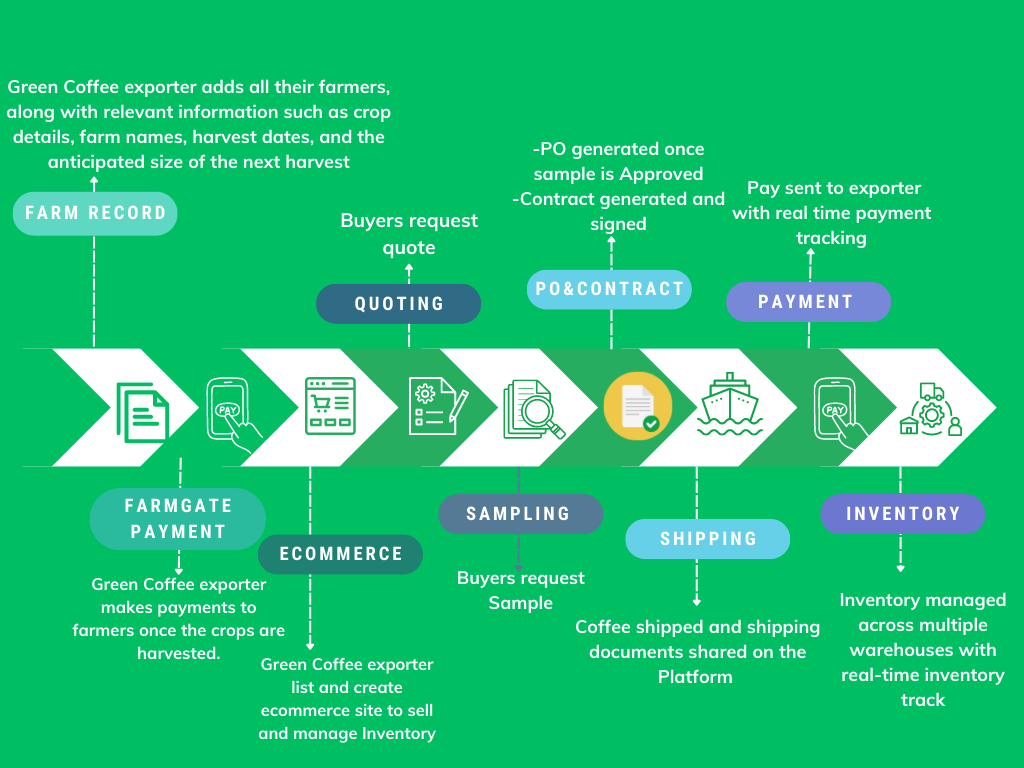
Overview of AGnimble’s Coffee procurement use case.
Future Outlook and Recommendations
As we look ahead, emerging technologies hold immense promise in shaping the future of agricultural procurement. Innovations such as artificial intelligence, Internet of Things, and robotics are revolutionizing the industry, offering unprecedented opportunities for efficiency and sustainability.
To fully capitalize on the potential of digital solutions, strategic scaling is vital. This involves creating an ecosystem that fosters collaboration and knowledge-sharing among stakeholders. Building robust digital infrastructure, investing in talent development, and promoting the adoption of standardized protocols will accelerate the integration of digital technologies across the agricultural value chain. It is crucial to identify champions within the industry and empower them to champion digital transformation initiatives.
Achieving a sustainable and resilient agricultural sector requires collaborative efforts among all stakeholders. Producers, buyers, governments, technology providers, NGOs etc must come together to share best practices, align interests, and co-create innovative solutions. Collaboration can drive the adoption of sustainable procurement practices, encourage responsible resource management, and ensure the well-being of communities involved. Together, we can build a resilient agricultural sector that nourishes both people and the planet.
- Nigeria’s Coffee Revolution: How JR Farms and Cross River State are Reviving Nigeria’s Lost Agricultural Heritage - June 16, 2025
- How B2B e-commerce will change the Agricultural commodity supply chain - December 13, 2023
- Understanding Africa Agriculture commodities export market and its opportunities - December 5, 2023
